Author: Jani Prinsloo & Liezl Kruger
Artificial Intelligence is causing many waves across the field of education, and instructional design is no exception. Instructional designers have seen how AI has enhanced their workflows by enhancing the way they brainstorm content ideas, write topic/lesson scripts and plan graphics and visuals for more engaging learning experiences.
This post looks at how AI tools (such as ChatGPT, TeacherMatic, and the AI Storyboard Generator) can enhance instructional design workflows while also highlighting the importance of human insight, pedagogy, and empathy in the process. It aims to clarify AI for Instructional designers and offer practical examples of where to integrate it effectively.
The Rise of AI in Instructional Design
Over the past few years, AI has shifted from a futuristic concept to a practical tool in the hands of Instructional designers and educators. This has caused significant pressure on higher education institutions, schools and corporate training centres to deliver high-quality, engaging, scalable, cost-effective learning experiences. As AI develops, people are beginning to realise how AI can serve as a partner in enhancing learning experiences. However, it is important to understand how AI and humans interact and how this partnership enhances the learning experiences of individuals within the AI-enabled learning ecosystem (Ch’ng, 2023).
Thinking Point:
Can AI enhance instructional design without replacing the Instructional designer?
What AI Brings to the Table
Speed and scalability: AI tools enhance the creation process through automating content outlines, creating quiz questions and answers and creating examples.
Tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity.ai are great for creating course outlines and examples. When creating prompts for these tools, the quality of your prompt will influence the output generated. The CORE format (Fiesel, 2025) is an example of how to structure prompts:
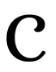
What is the learning context? For example, the learners are Grade 9 learners in a South African School, and the topic is The Cold War in the History Subject.) You can include websites or documents on which to base the course outline.

What format do you need the output to appear in? For example, providing the outline in bullet point format with different topics and a short explanation of what the topics are about. In the output, you can also set the writing style or tone, for example, using easy-to-understand language for 15-year-olds.
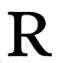
Providing the perspective from which the responses are generated. In the example presented above, an example of the role would be: “You are a Grade 9 History Teacher at a South African school…”
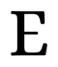
Provide an example of how you want the AI to respond. To build on the example of teaching the important events of the Cold War to Grade 9 learners, you would provide the following structure: Please create a timeline for the main events that led up to and followed the Cold War:
- Early Cold War (1947-1949). Provide a Creative Commons picture of Harry Truman.
- Height of the Cold War (1950-1963). Provide a Creative Commons image of Korea
To learn more about how to structure your prompting, the online article, Basic Prompt Structure and Key Parts provides easy-to-follow explanations and examples.
Content planning/ideation:
While AI chatbots (like ChatGPT and Perplexity.ai) can provide good basic questions and answers for quizzes based on prompts (and can even export the results in a specific required format, such as GIFT files for Moodle), there are tools specifically created for teachers by teachers who understand the complexities of the learning experience. An example is Teachermatic. Teachermatic has a library of hundreds of different generators that can streamline your work that would have taken hours to complete manually into a few minutes.
Examples of ready-to-use generators include:
- Multiple choice questions
- Lesson plans
- Lesson objectives
- Feedback generators
- Flash cards, and many
For a demonstration on the unique and time-saving features of Teachermatic, please contact us at hello@mmysolutions.co.za

Where Human Designers Are Irreplaceable
While AI tools can support and accelerate many aspects of the course development process, AI doesn’t eliminate the need for Instructional designers. There are a variety of ways to explain how AI make the Instructional designer role even more essential.
Here are a variety of ways, and below we name the most important few:
- Understanding the learners and their context – The Instructional designer applies empathy, cultural awareness, and knowledge about the learners’ context into the design process. Ensuring the course is relevant, inclusive, and accessible to all learners.
- Curating and validating the course content – Although AI generates the content for learning and teaching, the Instructional designer needs to analyse the draft materials, conduct fact-checks, ensure accuracy, appropriateness, and tone. Then the Instructional designer needs to adapt and refine the content to ensure it’s credible and of high quality before it can be finalised as usable for the course.
- Making ethical and inclusive design choices – The Instructional designer takes responsibility for making content accessible, fair, and representative of diverse perspectives, ensuring all learners are included by using language and making assumptions that do not exclude any learner and help learners feel seen and supported.
Some of the other ways ID’s role is essential include applying pedagogical principles and learning theories, as well as defining what learning goals and success look like in the course. AI is surely a tool that enhances teaching and learning but doesn’t replace the Instructional designer.
Best Practices for Instructional designers Using AI
The Instructional Designer’s Toolbox
While new AI tools are increasing every day, it is important to consider your AI workflow as an instructional designer. Some tools may be quick to use, but different tools excel in different aspects of content development. For example, one tool may be great at creating animations, but the available voices may not suit your specific needs. Therefore, you may need to use another tool to create the voice-over. Establish an effective workflow that allows you to work more productively while creating engaging, relatable and relevant content. Using apps and tools that allow for wider access and quick updates also improve the scalability and efficiency of your workflow.
The human element in content ideation and creation is undeniable, as it is necessary to critically review and refine the outputs created by the AI tool.
Conclusion
As we mentioned at the start of this post. AI is creating a lot of waves in education. As we’ve seen, these waves bring with it a variety of different opportunities to streamline workflows, spark critical thinking, enhance creativity and reimagine what’s possible in course development.
Reshaping the way we think about AI and what it brings to the Instructional design process is important. Considering how we utilise AI to brainstorm, map, create, develop, and deliver learning experiences is crucial.
In conclusion, AI cannot replace instructional designers, but Instructional designers can view AI as a valuable tool that helps them enhance their role as creators of learning experiences. As you explore AI tools like ChatGPT, TeacherMatic, and AI Storyboard Generators, remember that the goal isn’t to hand your instructional design process over to a machine. The idea is to use the machine to enhance it. AI can handle the repetitive, time-consuming tasks, allowing the Instructional designer to focus on creating learning experiences that help learners succeed.
References
Ch’ng, LK. (2023) How AI Makes its Mark on Instructional Design. Available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1410083.pdf
Fiesel, S. (2025) Mastering AI Prompt Engineering: The six Frameworks Marketers Need to know. Available at: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/mastering-ai-prompt-engineering-six-frameworks-marketers-scott-fiesel-mqmpe.
Kuka, V. (no date) Understanding prompt structure: key parts of a prompt. Available at: https://learnprompting.org/docs/basics/prompt_structure?srsltid=AfmBOopVec7HeZzT4LDnP702TDUgyu7tN4k81H1v1ACDcCXzsMGJ3oGG.